|
||
|
How do you identify them? Now, if you have a camera with aperture and shutter speed controls (a mode dial with PASM or P/Tv/Av/M) and you take it outside and half-press the shutter, two numbers should pop up: One might have an f in front of it (ie. f3.5) or it will be a decimal of sorts (ie. 4.0). That number is the aperture. The other number (if you're outside) should be larger, say around 200-4,000. That's the shutter speed. Aperture The aperture is the size of the lens opening. It controls the amount of light let in: a larger aperture lets in more light, while a smaller aperture lets in less light.   An aperture is made out of aperture blades (usually five to nine) that form a rough circle to control the size of the opening, and therefore the amount of light let in. The size of the opening is that f/number that I described earlier. Basically, that f/number is a ratio of focal length to aperture diameter. Do you need to know this? Not really, except you should keep in mind that the aperture is a ratio. Simply put, the smaller the f/number, the larger the opening (f/3.5 = 1/3.5 = 0.286; f/16 = 1/16 = 0.0625). That's all I'm going to explain here because it's an extremely complicated topic and you don't really need to know it. There's plenty of places on the web that explain it in great scientific detail; this is not one of them. The following is a diagram of f-stops. Each f-stop (or just a stop) lets in half the amount of light of the previous f-stop.  Now, lets get on to why this matters and how it can change what your picture looks like. Basically, a larger aperture (lower f/number) will have your subject in focus, and everything in front of and behind it blurry. A smaller aperture will have your subject in focus and everything in front of and behind it quite focused as well. Take a look at the following diagram; the further apart the lines are, the more out of focus something is: 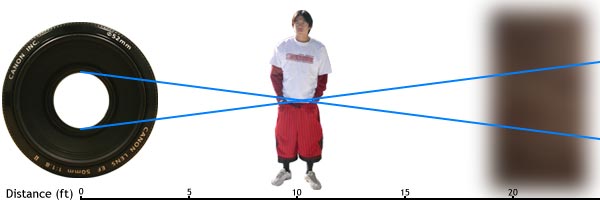 Large aperture (f/1.8).  Small aperture (f/16).  Summary: Large aperture, background out of focus; small aperture, everything in focus. (Large aperture = smaller f-number, small aperture = larger f-number). Shutter Speed Shutter speed is a much simpler concept to understand. It's basically how long the sensor/film in the camera is exposed to light. How long the shutter stays open depends on how much light there is. For pictures with the same aperture setting, if the is shutter open too long, the picture will be too bright, and if it's not open long enough, the scene will be too dark. Therefore, you control the overall exposure (lightness and darkness) of the scene with both the aperture and shutter speed control.  Your camera judges this for you, but you can manually set it as well. The shutter speed is the other (usually larger) number that isn't the aperture value. This number is actually a fraction, so if you see a shutter speed of 4000, it's actually 1/4000th of a second, while a value of 200 is 1/200th of a second. Now, remember how I mentioned stops in the aperture section? Well, they also apply to shutter speed, but in a slightly different way. By halving the time of exposure, you're letting in half the amount of light (so if you go from 1/2000 sec to 1/4000 sec, then you're letting in half the light). The opposite is true for doubling the exposure time. What you can do with shutter speed is freeze motion with a fast shutter speed or capture movement with a slow shutter speed. Flowing water looks silky smooth at speeds slower than 1/8th of a second (with a tripod), while you can freeze water in time with fast shutter speeds. The same thing goes for hip hop dancers.  Also, an important side note is that there is a rule for getting sharp images: 1/focal length. So if you have a 50mm lens then you'd need at least 1/50th of a second for your picture to not be blurry, and if you're using a digital SLR then there is a crop value (minus a few exceptions) of 1.5/1.6 so your 50mm lens is a 75~80mm lens, which means that you need a shutter speed of at least 1/80th of a second to get a sharp image. Summary: Fast shutter speed = freeze action. Slow shutter speed (w/ tripod) = silky flowing water. How Aperture and Shutter Speed are Related Aperture and shutter speed are bound together like an old married couple. For the same scene, if you open the aperture, you increase the shutter speed, and if you close down the aperture, you decrease the shutter speed. Think of a bucket of water with a hole in the bottom. If you have a large hole in the bottom of the bucket (large aperture), water will drain out quickly (fast shutter speed). Conversely, for the same amount of water, if you have a small hole in the bottom of the bucket (small aperture), the water will drain out slowly (slow shutter speed). 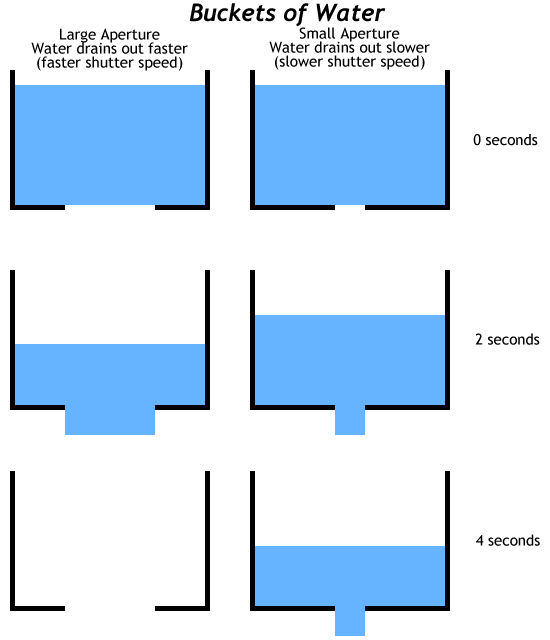 Remember how I mentioned stops earlier? Well one aperture stop is equivalent to one shutter speed stop, therefore if you open up your aperture one stop brighter (say from f/8 to f/5.6), and increased your shutter speed to one stop darker (like 1/250 to 1/500), then you would get the same exposure. So f/8 @ 1/250 is equivalent to f/5.6 at 1/500. This is the theory of equivalent exposures. Summary: Larger aperture, faster shutter speed; smaller aperture, slower shutter speed. Increase aperture by one stop and decrease shutter speed by one stop = equivalent exposure (and vice versa). There are a lot of uses for aperture and shutter speed. One of which is of course the background blur that everyone always wants to know how to get. Another thing you can do with a slow shutter speed is a night shot, which can give very interesting results. Check them out. |
||
Back to Main Digital camera help, tips on digital cameras, and camera techniques. Canon Powershot camera help and Nikon digital camera tips. Canon SLR and Canon camera tutorials. Nikon SLR, Panasonic, Casio, and Pentax digital camera technique. All content on these pages are Copyright 2007-2011 Yu Jiang Tham. No content from this website may be used or duplicated without express permission from the owner. Please email support@facethelight.com for more information. FaceTheLight.com is part of The Happywalrus Network - Get Free Stuff and Make Money! |